Leaves of the persimmon tree found to improve blood circulation
01/17/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
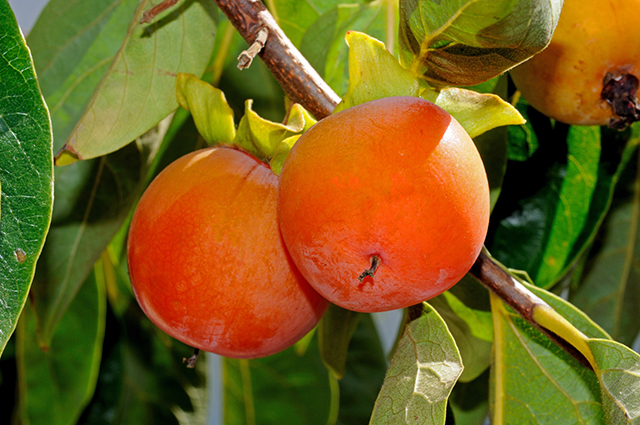

A team of South Korean researchers has discovered that the extract found in persimmon leaves may improve blood circulation. The study, which was published in the Journal of Medicinal Food, looked at the antiplatelet and anticoagulant properties of persimmon leaf extracts in vivo.
- For the study, the research team compared the effects of dietary supplementation with an ethanol extract of persimmon leaf with omega-3 fatty acids on blood coagulation, platelet activation, and lipid levels in vivo.
- They fed mice with a high-fat diet that contained either ethanol extract of persimmon leaf or omega-3 fatty acids for a period of nine weeks.
- They examined blood coagulation by observing the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) and prothrombin time.
- In addition, they assessed plasma thromboxane B2 (TXB2), serotonin, and soluble P-selectin levels.
- Results showed that the aPTT was greatly prolonged in the persimmon leaf extract and omega-3 supplement groups.
- The persimmon leaf extract reduced TXB2 level and decreased arterial serotonin transporter mRNA expression, but did not affect serotonin or soluble P-selectin levels.
- Both persimmon leaf extract and omega-3 fatty acids significantly reduced C-reactive protein and leptin levels.
- Both supplements also reduced total and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels.
- These results suggested that persimmon leaf extract may improve blood circulation by preventing blood coagulation and platelet activation as well as by decreasing cholesterol levels.
In conclusion, the findings of the study suggest that persimmon leaf extract may potentially be used to improve blood circulation.
To read more studies on supplements that help improve blood circulation like persimmon leaf extracts, visit SupplementsReport.com.
Journal Reference:
Ryu R, Kim H-J, Moon B, Jun UJ, Lee M-K, Lee DG, Ryoo ZY, Park YB, Choi M-S. ETHANOL EXTRACT OF PERSIMMON TREE LEAVES IMPROVES BLOOD CIRCULATION AND LIPID METABOLISM IN RATS FED A HIGH-FAT DIET. Journal of Medicinal Food. 25 June 2015; 18(7): 715-723. DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2014.3307
Tagged Under: blood circulation, blood flow, clotting, coagulation, lipid metabolism, persimmon, persimmon leaves, persimmon tree leaves, platelet activation, supplements